Last Week in AI #323 - Sonnet 4.5, Sora 2, Vibes, SB 53
Anthropic releases Claude Sonnet 4.5, OpenAI announces Sora 2 with AI video app, and more!
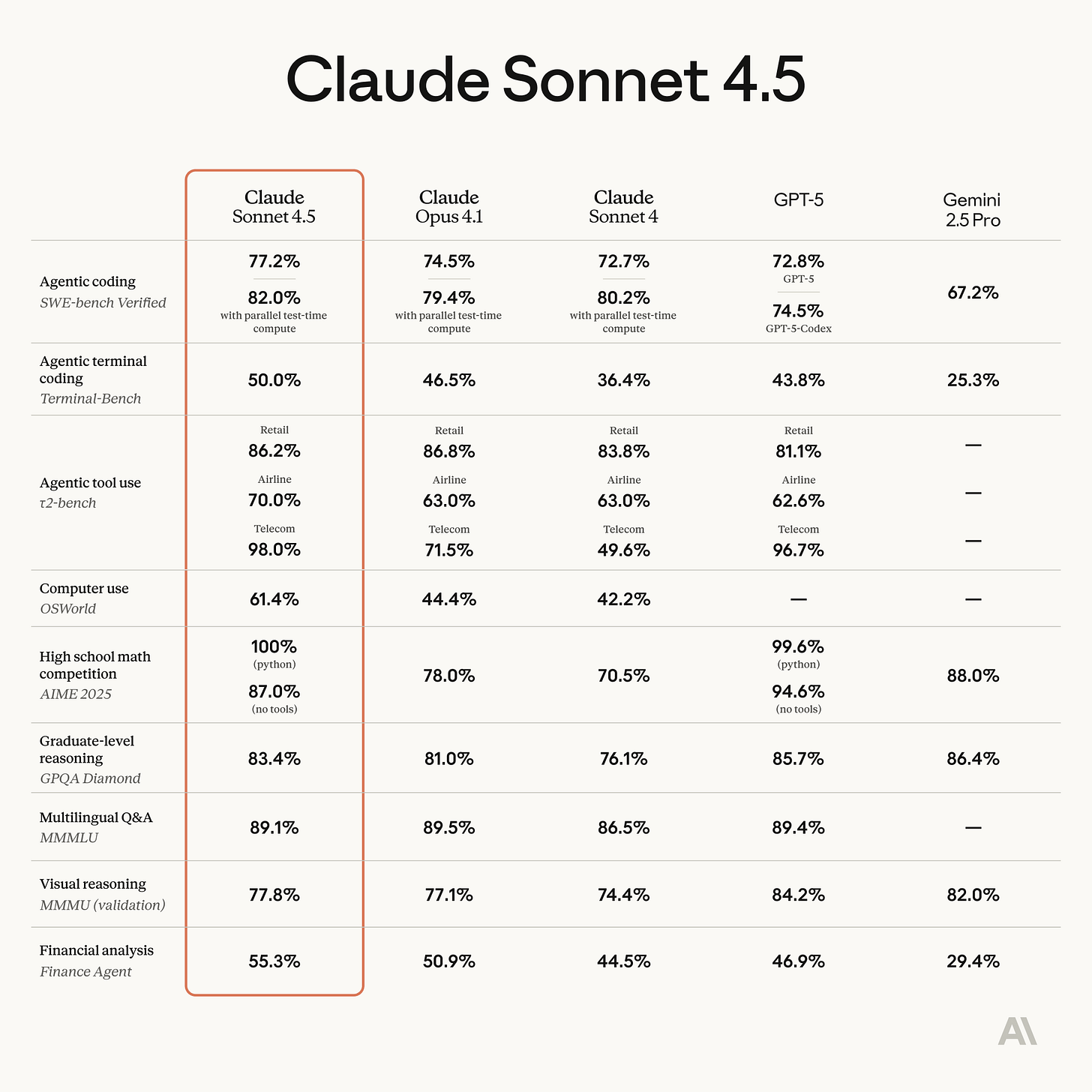
Anthropic releases Claude Sonnet 4.5
Anthropic announced Claude Sonnet 4.5, highlighting a major leap in autonomous “computer use” and coding capabilities. In internal tests, the model ran unattended for 30 hours to build a Slack/Teams-like chat app, generating ~11,000 lines of code, up from Opus 4’s seven-hour autonomy earlier this year. Anthropic claim…