Last Week in AI #335 - Opus 4.6, Codex 5.3, Gemini 3 Deep Think, GLM 5, Seedance 2.0
A crazy packed edition of Last Week in AI! Plus some small updates.
Editor’s note: I apologize for the inconsistent release date of the newsletter and podcasts in recent months. I’ll aim to start releasing on Saturday/Sunday consistently from now on! This edition of the newsletter covers a bit more than a week as a result.
I am also going to be adding an ‘Editor’s Take’ for Top News to add a bit commentary and extra context beyond the news summary.
Top News
Anthropic releases Opus 4.6 with new ‘agent teams’
Related:
Summary: Anthropic released Claude Opus 4.6, a major upgrade focused on larger, faster, and more collaborative work. The headline feature is “agent teams,” a research-preview capability that lets multiple coordinated agents split a complex task into parallel subtasks, communicate directly, and finish faster than a single sequential agent. Opus 4.6 also expands the context window to 1 million tokens (on par with Sonnet 4/4.5), enabling work over large codebases and long documents. Another key addition is a native PowerPoint side panel, letting users draft and edit slides directly inside PowerPoint with Claude instead of generating decks externally and importing them.
Anthropic says Opus has evolved from a coding-first model to one suited for a broader set of knowledge workers, citing adoption beyond software engineers to product managers and financial analysts. Advancements in Claude Code and the productivity suite Claude Cowork are feeding a shift from “vibe coding” to “vibe working,” reflecting end-to-end task execution and higher-quality professional outputs.
Editor’s Take: Opus 4.6 comes only a few months after 4.5, and yet showcases impressive gains across a variety of benchmarks beyond what the 0.1 version bump might suggest. It feels like the frontier labs may have gotten to the point of continously post-training their models via RL, and I wouldn’t be surprised if we see more impressive gains in just a few months.
With GPT-5.3-Codex, OpenAI pitches Codex for more than just writing code
Related:
OpenAI’s new Spark model codes 15x faster than GPT-5.3-Codex - but there’s a catch
A new version of OpenAI’s Codex is powered by a new dedicated chip
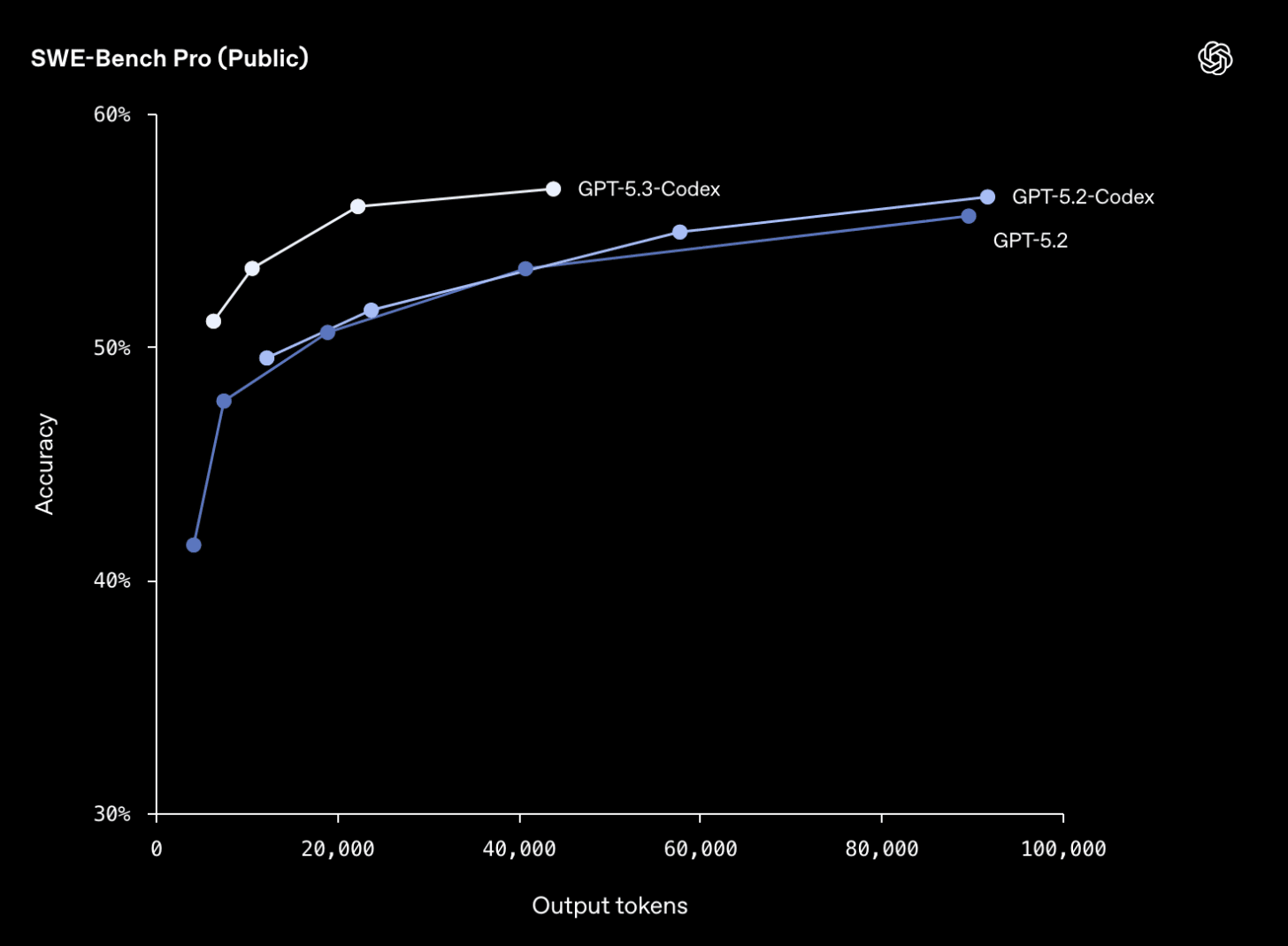
Summary: OpenAI unveiled GPT-5.3-Codex, a frontier coding model available via CLI, IDE extension, web, and a new macOS Codex app (API coming later). The model outperforms GPT-5.2-Codex and GPT-5.2 on SWE-Bench Pro and Terminal-Bench 2.0, and runs 25% faster with lower compute usage. While headlines claim it “built itself,” OpenAI clarifies the model was “instrumental in creating itself,” with early versions used to debug training, manage deployments, analyze test results, clean datasets, and monitor training runs—not fully self-building. The model is pitched for the full software lifecycle beyond code generation: debugging, deploying, monitoring, writing PRDs, editing copy, user research, tests, and metrics. OpenAI also designated GPT-5.3-Codex as its first “high-capability” model for cybersecurity per its Preparedness Framework.
A companion release, GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, targets real-time “conversational” coding with a smaller, latency-first research preview that generates code up to 15x faster than GPT-5.3-Codex but trails it on SWE-Bench Pro and Terminal-Bench 2.0, and is not expected to meet the “high-capability” cybersecurity threshold. Spark achieves big latency gains—roughly 80% lower round-trip overhead, 50% faster time-to-first-token, and 30% lower per-token overhead—via session and streaming optimizations and persistent WebSocket connections, and it defaults to lightweight, targeted edits without auto-running tests. Initially limited to $200/month Pro users, Spark is the first milestone in OpenAI’s multi-year, >$10B partnership with Cerebras, running inference on the WSE-3 waferscale chip (4 trillion transistors).
Complementing the models, OpenAI’s new macOS Codex app orchestrates multiple agentic coding assistants in parallel, supports scheduled automations and selectable agent “personalities,” and has seen 500,000+ downloads, with OpenAI aiming toward dual modes: long-horizon reasoning/execution alongside real-time collaboration, and background sub-agents for longer tasks.
Editor’s Take: OpenAI seems to have succesfully caught up with Anthropic in terms of having a model that is optimized for improving workplace productivity, after having previously focused more on improving ChatGPT as a general purpose chatbot for anybody and everybody. Pretty big deal!
Google Unveils Gemini 3 Deep Think for Science & Engineering
Related:
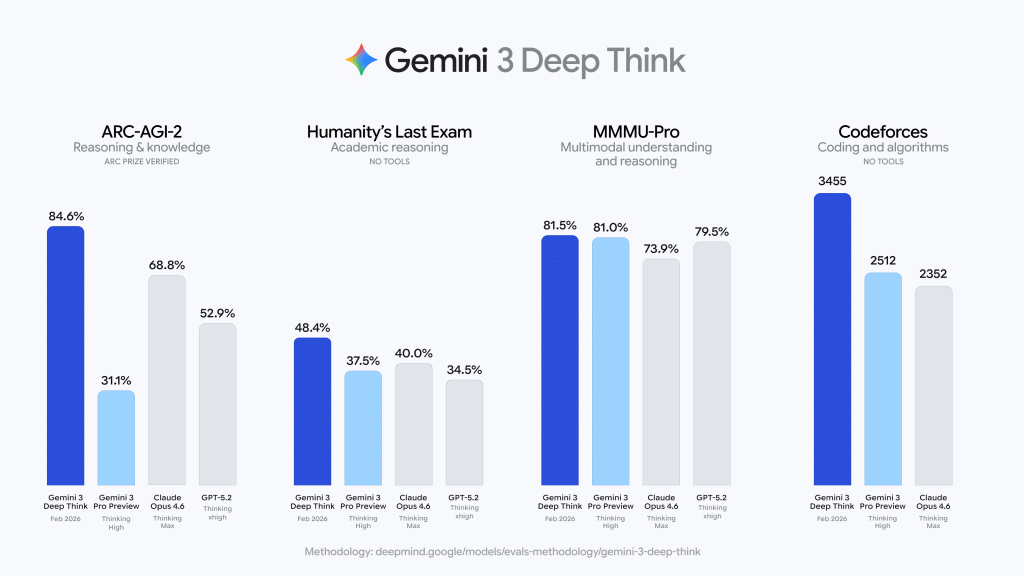
Summary: Google unveiled a major upgrade to Gemini 3 Deep Think, a specialized “extended reasoning” mode tuned for science, research, and engineering where accuracy and multi-step logic matter more than latency. The system emphasizes test-time compute—letting the model think longer—and internal verification to prune incorrect reasoning paths, a direct response to competitors like OpenAI’s o1 and Anthropic’s Claude. Google reports a verified 84.6% on ARC-AGI-2 from the ARC Prize Foundation, a benchmark designed for generalization to novel tasks rather than memorization, and 48.4% on Humanity’s Last Exam without tools across logic-dense academic questions. Deep Think also claims gold medal–level performance on the written sections of the 2025 International Physics and Chemistry Olympiads and gold-level on the 2025 IMO, plus 50.5% on the CMT-Benchmark for advanced theoretical physics.
For engineering and coding, Gemini 3 Deep Think now posts a 3455 Elo on Codeforces—“Legendary Grandmaster” territory—demonstrating capability in complex data structures, algorithmic optimization, and system design, with Google noting a 35% accuracy lift in software engineering tasks over prior versions.
Editor’s Take: rounding off the impressive model releases, this one may just be the most impressive of all. Even having gotten used to major advancements, the ARC-AGI-2 result surprised me and many other commentators. Similar to Opus 4.6, this makes me wonder if scaling up RL / post-training is behind such rapid and signifiacnt improvements.
DeepSeek boosts AI model with 10-fold token addition as Zhipu AI unveils GLM-5
Related:
Zhipu leads rally in Chinese AI stocks, surging 30% as a wave of new releases hits market
MiniMax M2.5 promises “intelligence too cheap to meter” as Chinese labs squeeze Western AI pricing
China’s Zhipu AI launches new major model GLM-5 in challenge to its rivals
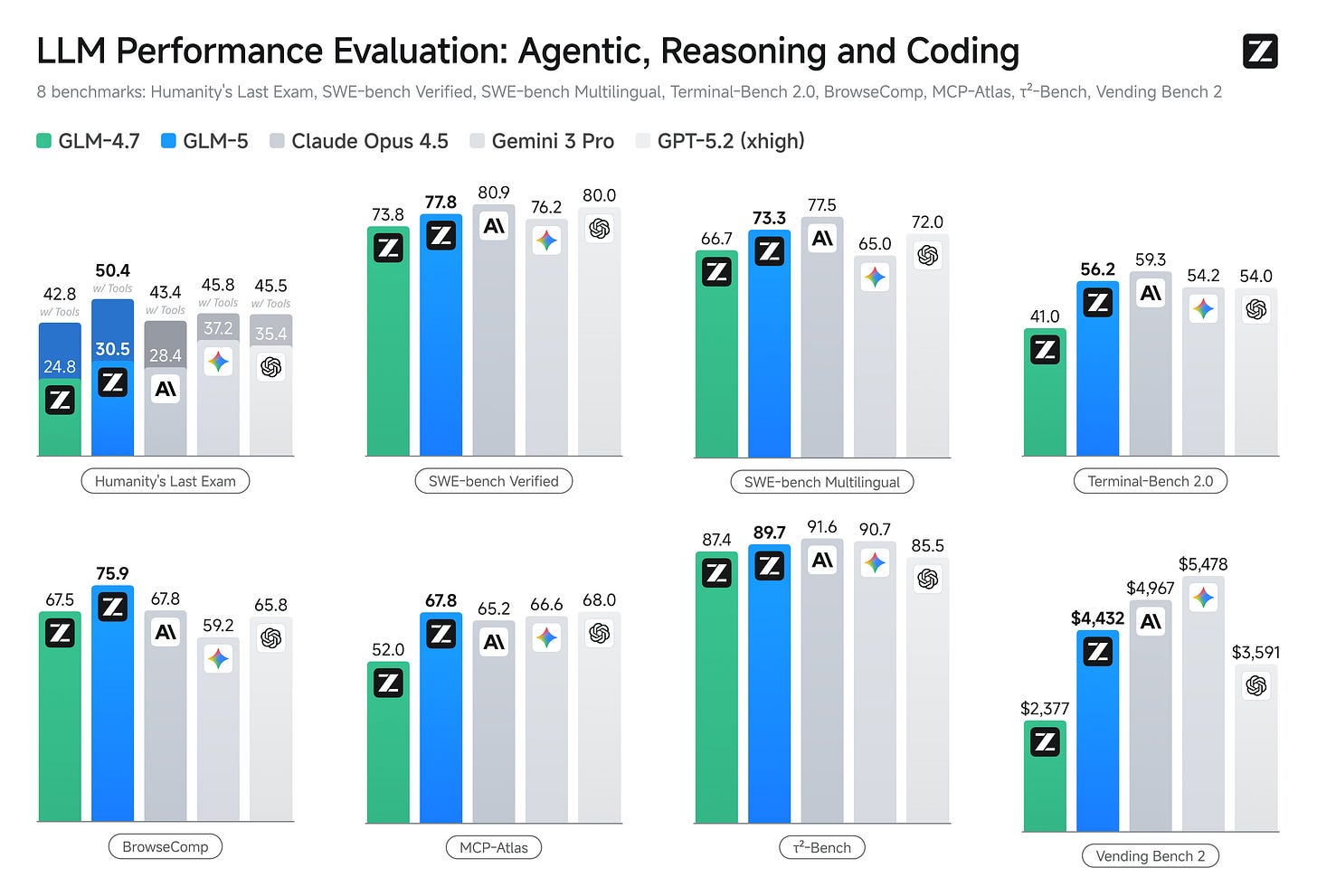
Summary: China’s AI labs rolled out major upgrades focused on long context, coding, and agentic workflows. DeepSeek expanded its flagship model’s context window from 128,000 to over 1,000,000 tokens, enabling much larger “memory” for complex reasoning, multi-file code work, and sustained tasks. Zhipu AI (Z.ai) launched GLM-5, an open-weight flagship positioned for “agentic engineering” rather than “vibe coding,” emphasizing end-to-end software delivery, deep debugging, and multi-step tool use. GLM-5 scales to a Mixture-of-Experts architecture with roughly 744B total parameters and 40B active per token, increases pretraining to 28.5T tokens, and integrates DeepSeek Sparse Attention to balance long-context performance with serving efficiency.
Benchmarks and pricing underscore intensifying competition. Zhipu reports GLM-5 leads among open models on coding and agentic tasks, with self-reported scores like 77.8 on SWE-bench Verified and strong showings on BrowseComp and MCP-Atlas; it ranks #1 among open models in Text Arena and aims to approach Claude Opus 4.5, though it still lags Anthropic’s Claude on coding by Zhipu’s own admission. MiniMax released M2.5 under MIT as open weights, trained with reinforcement learning across hundreds of thousands of complex environments to optimize autonomous planning and long-horizon efficiency.
Editor’s Take: Starting with DeepSeek V3/R1, it has felt like the open source models coming out of China are getting increasingly close to matching the performance of the flagship models of western frontier labs. These releases continue that trend, which makes me wonder if open source options will soon start eating away at the profits of closed source API providers.
Bytedance shows impressive progress in AI video with Seedance 2.0
Related:
ByteDance’s new model sparks stock rally as China’s AI video battle escalates
ByteDance’s Seedance 2.0 Might be the Best AI Video Generator Yet
ByteDance’s new model sparks stock rally as China’s AI video battle escalates
Hollywood isn’t happy about the new Seedance 2.0 video generator
Summary: ByteDance pre-released Seedance 2.0 to select users, showcasing a multimodal video generator that accepts up to 12 inputs at once (max: nine images, three videos, three audio files) alongside text, and outputs 4–15s clips with auto-generated sound effects/music. The headline upgrade is precise reference capability: users can lift camera motion, editing grammar, effects, and action beats from uploaded reference videos, swap/insert characters, extend existing shots, and chain multi-scene storylines while maintaining style and character consistency. Early testers report sharper 2K exports, roughly 30% faster generation vs Seedance 1.5, smoother camera moves, improved visual consistency, and convincing motion accuracy and lip-sync, with results that are watermark-free.
The launch intensified China’s AI video race days after Kuaishou’s Kling 3.0 and sparked a stock rally: COL Group hit its 20% limit, Shanghai Film and Perfect World rose ~10%, and Huace Media ~7%, while the CSI 300 ticked up 1.63%. Swiss consultancy CTOL and other reviewers claim Seedance 2.0 surpasses OpenAI’s Sora 2 and Google’s Veo 3.1 in practical tests, citing lifelike characters, fine-grained edit control, and “cinematic” natural-language workflows—though cherry-picked demos likely show best-case output.
Meanwhile, Hollywood and rights groups blasted the tool’s lack of guardrails after viral clips mimicked celebrities (e.g., Tom Cruise vs. Brad Pitt) and Disney/Paramount IP; Disney and Paramount sent cease-and-desist letters alleging indistinguishable reproductions of franchises like Spider-Man, Darth Vader, and Grogu.
Editor’s Take: this feels like a Nano-Banana moment for video generation — (I created that em-dash, not AI) a huge and sudden leap far beyond what existing text-to-video models can do. The ability to edit/compose inputs so well vastly increases the usefulness of this model, and I wouldn’t be surprised if we start seeing a lot more primarily AI-generated videos within a year.
Anthropic says ‘Claude will remain ad-free,’ unlike ChatGPT
Related:
Summary: Anthropic announced Claude will remain ad-free, contrasting OpenAI’s plan to insert clearly labeled ads for ChatGPT free and Go users. Anthropic’s blog says sponsored links and product placements won’t appear or influence responses, citing conflicts with health advice and productivity use cases, though it left a door open to revisit the stance later. The company aired multiple Super Bowl spots parodying ad-interrupting AIs, including a 30-second in-game ad and a 60-second pregame version featuring an ad-enabled AI therapist.
Editor’s Take: honestly more amusing than significant, though OpenAI’s incredibely defensive response perhaps hints at some anxiety regarding public perception of ChatGPT’s adoption of ads for non-paying users.
Other News
Tools
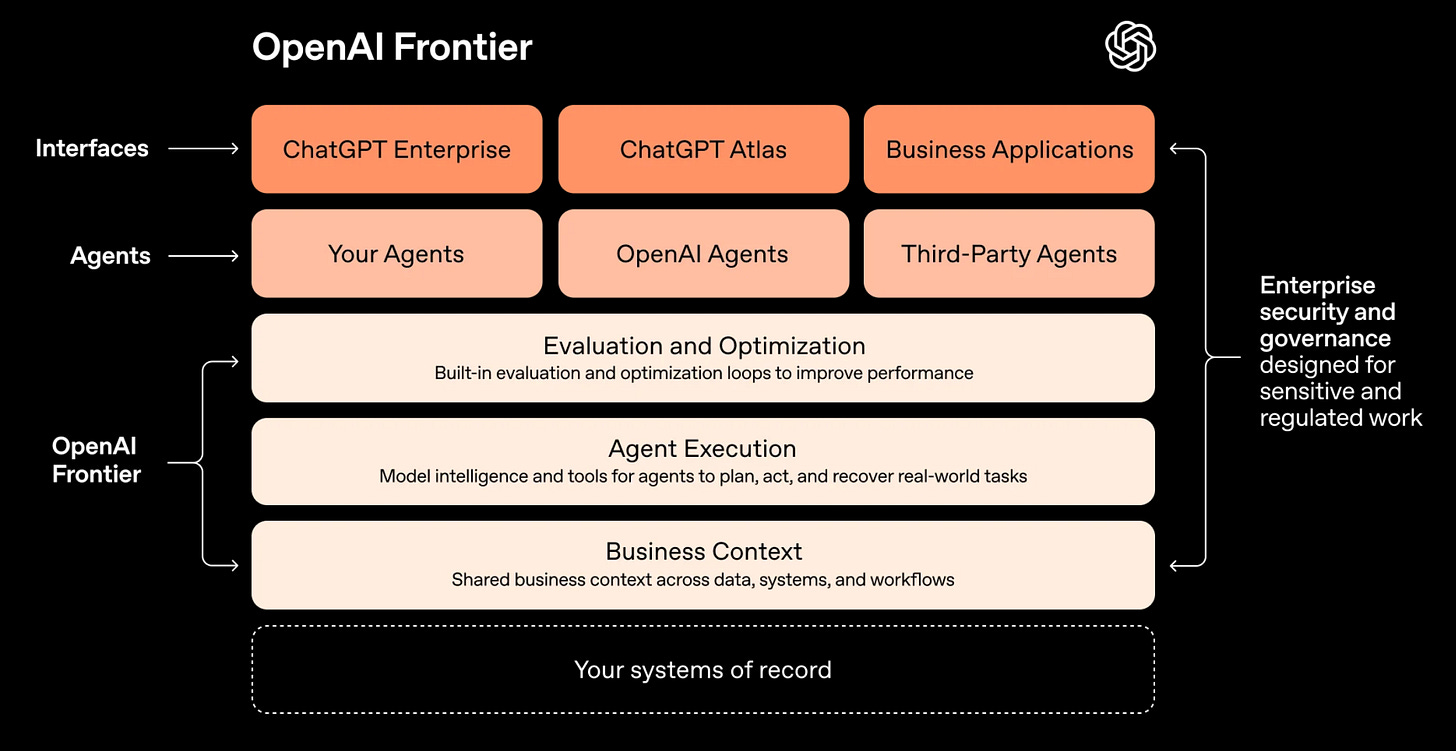
OpenAI Frontier is a single platform to control your AI agents. It provides a centralized interface that connects and governs AI agents (from OpenAI or third parties) across enterprise systems, lets teams onboard and evaluate agents, stores agent memories, and is rolling out to a limited set of customers with broader availability planned.
xAI launches Grok Imagine API for text and image to video. The API supports 1–15 second clips at 480p or 720p with multiple aspect ratios, plus prompt-driven edits that keep source duration while enabling restyling, object changes, and motion control.
Qwen Team Releases Qwen3-Coder-Next: An Open-Weight Language Model Designed Specifically for Coding Agents and Local Development. It uses a sparse MoE hybrid-attention architecture (80B total, ~3B active per token) and agentic RL training on ~800K executable tasks to enable long-horizon planning, tool calling, test execution, and competitive benchmark performance.
GitHub adds Claude and Codex AI coding agents. GitHub is adding Anthropic’s Claude and OpenAI’s Codex as optional coding agents inside GitHub (including Mobile and VS Code) for Copilot Pro Plus and Enterprise users, enabling developers to assign agents to tasks, compare outputs, and consume premium requests.
Cursor launches Composer 1.5 with upgrades for complex tasks. Composer 1.5 increases reinforcement learning scale and adds ‘thinking tokens’ plus recursive self-summarization to improve planning and maintain accuracy on longer, more complex coding tasks.
China’s ByteDance, Alibaba unveil AI image tools to rival Google’s popular Nano Banana. ByteDance and Alibaba each released new image-generation models—Seedream 5.0 and Qwen-Image-2.0—that they say offer better prompt understanding, edit controls, and cost or speed advantages compared with Google’s Nano Banana Pro.
Business
Humanoid robot startup Apptronik has now raised $935M at a $5B+ valuation. The new influx of capital, including follow-on investments from Google and Mercedes-Benz, brings the Series A to $935M and values Apptronik at about $5.3B while funding development of its Apollo humanoid for warehouse and industrial tasks using embodied AI.
Nvidia-backed AI voice startup ElevenLabs hits $11 billion valuation in fresh fundraise, as it eyes IPO. The funding round, led by Sequoia with participation from existing and new investors including Nvidia, values ElevenLabs at $11 billion after it reported over $330 million in ARR and plans to expand its product suite and pursue an IPO.
AI video startup Runway raises $315M at $5.3B valuation, eyes more capable world models. The financing will support Runway’s push to pre-train more capable world models, expand into industries like gaming, robotics, medicine, and climate, scale its infrastructure and team, and commercialize its Gen 4.5 video model with native audio and long-form generation.
Okay, now exactly half of xAI’s founding team has left the company, Musk addresses wave of departures from xAI. Half of the founding team has left amid a string of recent departures—some amicable, others tied to technical issues, product controversies, and competitive pressures—that raise concerns about xAI’s ability to retain talent ahead of an IPO. Musk said the company was reorganized to speed execution.
OpenAI disbands mission alignment team. OpenAI reassigned the six- to seven-person mission-alignment group to other roles while appointing its former leader, Josh Achiam, as “chief futurist” to study how AI and AGI will shape the world.
Anthropic raises another $30B in Series G, with a new value of $380B. The funding round, led by GIC and Coatue and joined by investors like D.E. Shaw Ventures, Founders Fund, Accel, and the Qatar Investment Authority, boosts Anthropic’s valuation to $380 billion as it races to expand enterprise-focused Claude amid competition from OpenAI.
Research
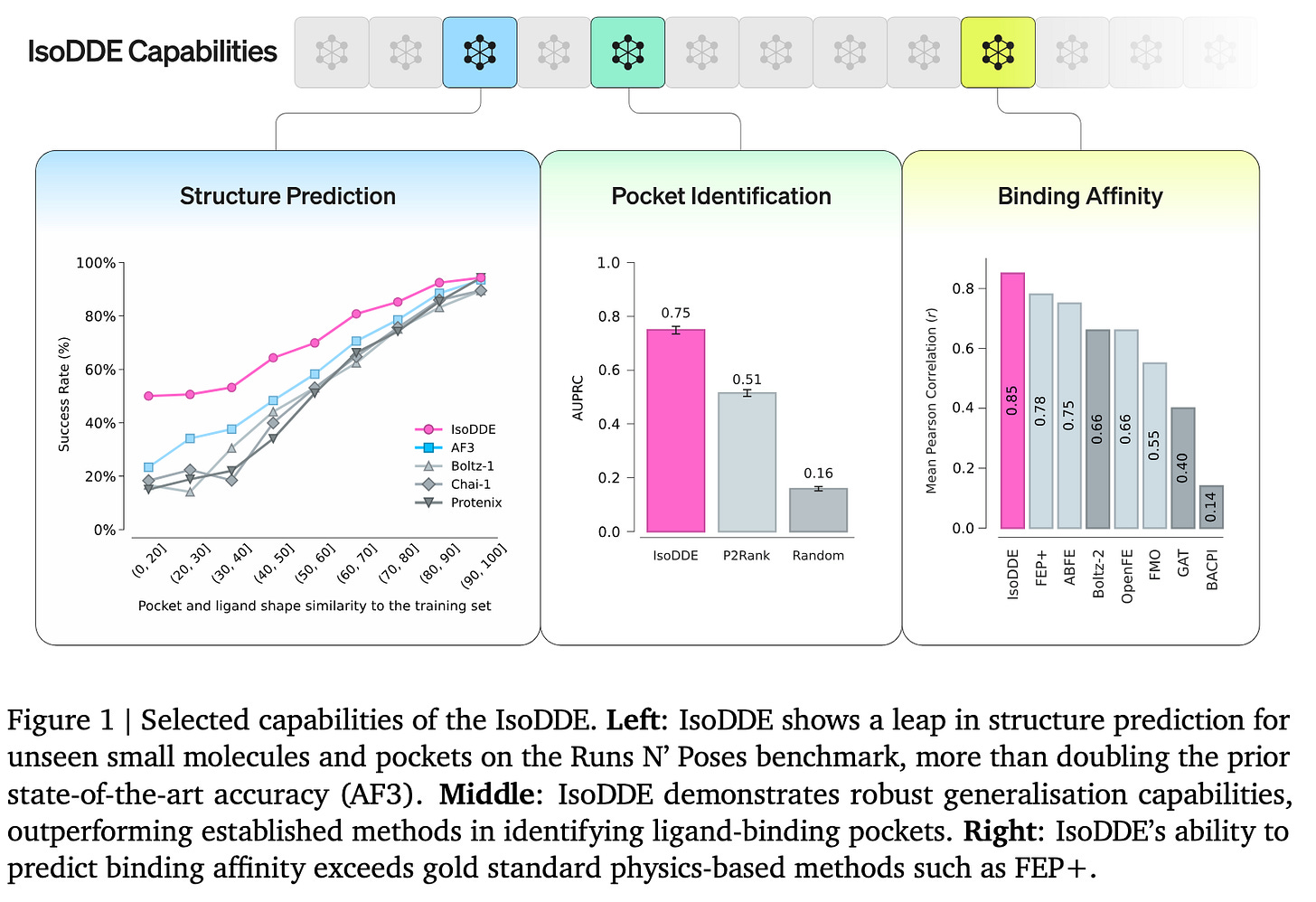
Google’s AI drug discovery spinoff Isomorphic Labs claims major leap beyond AlphaFold 3. The system reportedly identifies novel docking sites and predicts protein-ligand binding strength far faster and cheaper than traditional methods, doubling AlphaFold 3’s accuracy on out-of-distribution complexes and already being used internally to aid drug candidate discovery.
POPE: Learning to Reason on Hard Problems via Privileged On-Policy Exploration. The method uses oracle solutions as privileged on-policy demonstrations during training to guide exploration and policy updates on difficult reasoning tasks, improving the model’s ability to learn hard problem-solving behaviors.
Saddle-to-Saddle Dynamics Explains A Simplicity Bias Across Neural Network Architectures. The authors show how a universal mechanism—recursively embedded saddle points connected by invariant manifolds—causes networks to learn solutions by sequentially recruiting effective units, producing stage-like training dynamics whose notion of simplicity is the minimal number of units (e.g., neurons, kernels, or heads) needed to express a solution.
KL-Regularized Reinforcement Learning is Designed to Mode Collapse. The authors prove that common KL-regularized objectives and hyperparameters often yield a unimodal, low-diversity optimal policy, outline conditions for multimodality, and provide a simple fix to recover diverse solutions.
Rethinking the Trust Region in LLM Reinforcement Learning. The paper argues that replacing PPO’s sample-ratio clipping with direct divergence-based constraints (implemented efficiently via Binary and Top-K approximations) yields more stable and effective LLM fine-tuning by avoiding over-penalization of rare tokens and under-penalization of common ones.
How Do Transformers Learn to Associate Tokens: Gradient Leading Terms Bring Mechanistic Interpretability. The authors analyze gradient leading terms to explain how transformer components develop token associations, offering a mechanistic interpretability perspective despite the paper metadata being unavailable on Hugging Face.
Deriving Neural Scaling Laws from the statistics of natural language. The paper shows that the exponent of neural data-scaling laws for language models can be predicted directly from two measurable properties of natural language—the decay of next-token conditional entropy with context length and the decay of token–token correlations with temporal separation—and validates these predictions against GPT-2 and LLaMA-style training on real datasets.
F-GRPO: Don’t Let Your Policy Learn the Obvious and Forget the Rare. F-GRPO introduces difficulty-aware scaling to group-relative advantage estimates that reduces sharpening of solution diversity at common group sizes, improving high-budget pass@k and OOD accuracy without extra rollouts.
Retrieval-Aware Distillation for Transformer-SSM Hybrids. The method identifies and preserves only the attention heads that perform retrieval (G&A heads), replacing the rest with SSM recurrent heads and distilling to produce hybrids that match Transformer retrieval performance while cutting attention and SSM state memory by large factors.
Policy
ChatGPT will be available to 3 million military users on GenAI.mil. The platform will give the Defense Department’s roughly 3 million uniformed, civilian, and contractor users access to a custom, government-hosted ChatGPT instance (alongside Grok and Gemini) that keeps processed data isolated from public OpenAI models and is approved for sensitive-but-unclassified use.
Analysis
AI Doesn’t Reduce Work—It Intensifies It. Rather than cutting hours, firms are increasing employee AI use to boost productivity by applying tools to more tasks, which often adds responsibilities like overseeing outputs and integrating AI into workflows.


Thanks team for another excellent curation and critique of what's been happening in AI. I find your editors' summaries especially helpful to cut through the hyperbole. From my own testing of Claude Opus 4.6, I agree entirely that the change from 4.5 is quite dramatic, and project mode alone in Claude Code has improved massively.
https://thefoundersproduct.substack.com/p/on-consulting-and-new-opportunity?r=7uy5s2&utm_medium=ios